India, the world’s second-most populous nation, has embarked on an ambitious journey to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070. A critical aspect of this transition is addressing financed emissions, which are the greenhouse gas emissions associated with the investments and lending activities of financial institutions. These emissions, often indirect, stem from the activities of companies or projects financed by these institutions.
What are Financed Emissions?
Financed emissions refer to the greenhouse gas emissions associated with the investments and lending activities of financial institutions. These emissions are often indirect, as they stem from the activities of the companies or projects that financial institutions finance.
Consider a bank lending money to a coal power plant. The emissions generated by the plant are a result of the bank’s financial support, thus contributing to the bank’s financed emissions.
As the world moves towards a net-zero future, the role of financed emissions in achieving climate targets is gaining prominence, especially in rapidly developing economies like India.
Why are Financed Emissions Important for India?
India, with its ambitious climate goals and burgeoning economy, is at a critical juncture. India’s financial sector plays a vital role in driving economic growth. But this growth often comes at an environmental cost, with a significant portion of financing directed towards carbon-intensive industries. By addressing financed emissions, Indian banks and financial institutions can significantly contribute to the country’s path to net-zero emissions.
Average ESG Score vs Transparency Score
(Comparison between Indian and Global Financial Companies) Source: ISS
Source: ISS
Challenges in Managing Financed Emissions
The management of financed emissions presents several challenges for financial firms. Firstly, there is a need for robust data and methodologies to accurately measure and attribute emissions to financed activities. Additionally, banks must navigate the complexities of climate regulation and align their strategies with evolving global standards.
- Regulation: While progress is being made globally, India needs robust regulations that incentivize financial institutions to consider climate risks and promote financing for sustainable projects.
- Data and Transparency: Accurate data on financed emissions is essential for effective management. Collaborations between financial institutions, regulators, and industry experts can improve data collection and transparency.
- Scaling Clean Energy Finance: India needs significant investments in clean energy infrastructure to transition away from fossil fuels. Innovative financing models, like blended finance (which combines public and private capital), can play a crucial role in mobilizing the required capital.
- Sector-Specific Strategies: Different sectors have unique challenges and opportunities. Developing specialized financial institutions focused on specific sectors can foster targeted financing for clean technologies and sustainable practices.
The Role of Banking & Financial Sectors in Addressing Financed Emissions
Banks and lending companies play a pivotal role in the global effort to combat climate change, particularly through the management of financed emissions. As financial intermediaries, banks have the power to influence the carbon footprint of various sectors by directing capital toward sustainable projects and away from high-emission activities.
Here’s how the financial institutions and banks can help with financed emissions:
1. Risk Management and Portfolio Decarbonization:
- Climate Risk Assessment: Banks need to integrate climate risk assessment into their loan appraisal processes. This involves evaluating the vulnerability of potential borrowers to climate change impacts and the long-term viability of carbon-intensive projects.
- Portfolio Decarbonization Strategies: Develop strategies to gradually reduce the exposure of loan portfolios to high-emitting sectors. This can involve phasing out financing for new high-emission projects and offering incentives for existing borrowers to transition toward cleaner technologies
2. Aligning Portfolios with Climate Goals:
- Portfolio Screening: Banks can screen their portfolios to identify high-emission assets and sectors. This enables them to make informed decisions about divestment and reallocation of capital.
- Sustainable Finance Products: Offering green bonds, sustainable loans, and other financial products that support low-carbon projects can help banks and institutions reduce their financed emissions. These products can incentivize borrowers to adopt environmentally friendly practices.
- Impact Investing Initiatives: Partner with institutions offering impact investment opportunities in clean technologies and climate solutions. This allows banks to contribute to environmental goals while achieving financial returns.
- Conditionality: By incorporating environmental criteria into lending decisions, banks can encourage companies to adopt sustainable practices. For example, they can offer favourable loan terms to companies with strong environmental performance.
Average Portfolio Carbon Footprint vs Average Portfolio Decarbonisation
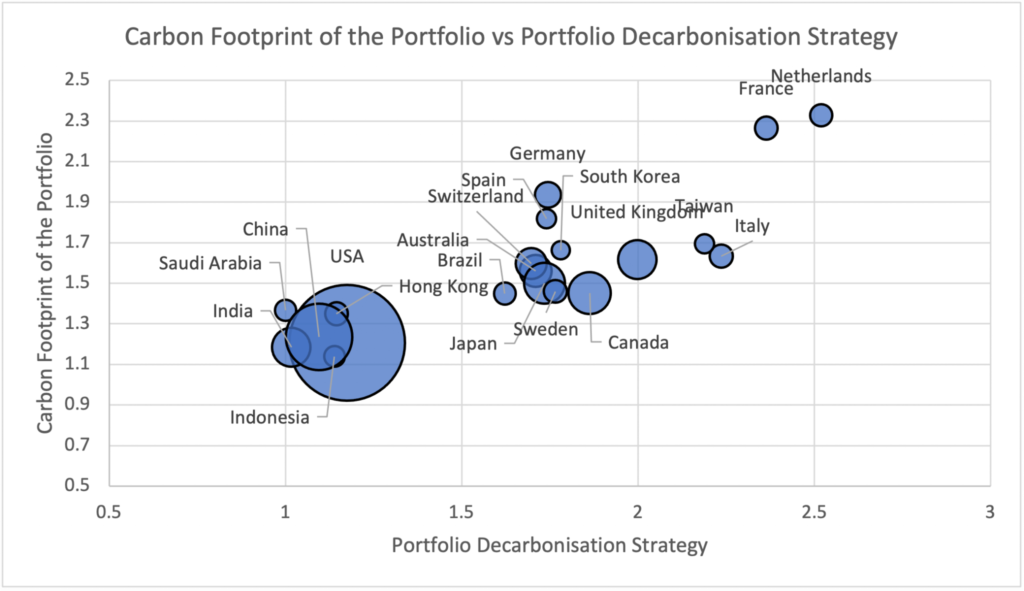
3. Transparency and Disclosure:
- Financed Emissions Reporting: Banks should adopt standardized methodologies to calculate and disclose their financed emissions. This transparency allows stakeholders to assess banks’ climate performance and hold them accountable for progress.
- Transparency: By disclosing their financed emissions, banks can provide stakeholders with a clear understanding of their climate impact. This transparency is essential for accountability and for tracking progress towards emission reduction targets.
- Advisory Services: Banks can provide advisory services to help portfolio companies develop and implement sustainability strategies. This includes guidance on reducing emissions, transitioning to renewable energy, and enhancing environmental performance.
4. Building Capacity and Collaboration:
- Internal Capacity Building: Invest in training and skill development for bank staff on climate finance and risk assessment. A climate-literate workforce is crucial for the effective implementation of sustainable finance strategies.
- Collaboration with Stakeholders: Partner with government agencies, industry associations, and NGOs to develop robust regulatory frameworks for climate finance. Collective action strengthens the overall impact of individual efforts.
- Policy Advocacy: Engaging in policy advocacy to support regulatory frameworks that promote sustainable finance and climate action can amplify the impact of banks’ efforts.
5. Supporting the Transition to a Low-Carbon Economy:
- Investment in Clean Energy: Banks can allocate capital to renewable energy projects, such as wind and solar power, to support the transition to a low-carbon economy.
- Innovation Financing: Providing funding for innovative technologies and solutions that reduce emissions, such as carbon capture and storage or energy efficiency measures, can further contribute to climate goals.
The Way Forward
Addressing financed emissions is a complex challenge, but it is a necessary step for India to achieve its net-zero goals. Collaborative efforts from financial institutions, policymakers, and industry leaders are crucial for developing robust frameworks, promoting transparency, and scaling up clean energy financing. By doing so, India can not only reduce its carbon footprint but also unlock new opportunities for sustainable growth.
Conclusion
As India advances towards its net-zero ambitions, the commitment of the financial sector to managing and reducing financed emissions will be instrumental in ensuring a sustainable future. Integrating climate considerations into their operations, financial products, and client engagements allows banks to contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the achievement of net-zero targets.
Explore our sustainable finance solutions and learn how we can help you achieve your climate goals.



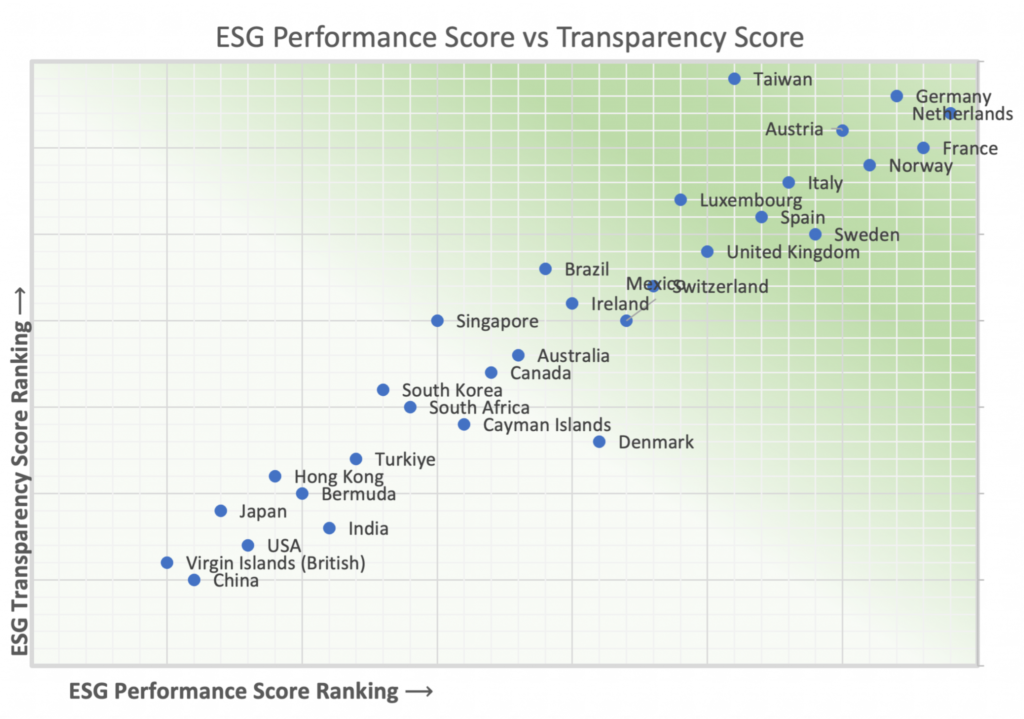 Source: ISS
Source: ISS



